TreeMap & TreeSet
Java TreeMap & TreeSet
最近工作,回顾一下,写个笔记。 基于openjdk1.8
最前面
二者底层结构均由二叉树实现,且默认有序,可实现comparator。
TreeMap
TreeMap 源码比HashMap多了622行,也内设了一些非常便利的方法调用。
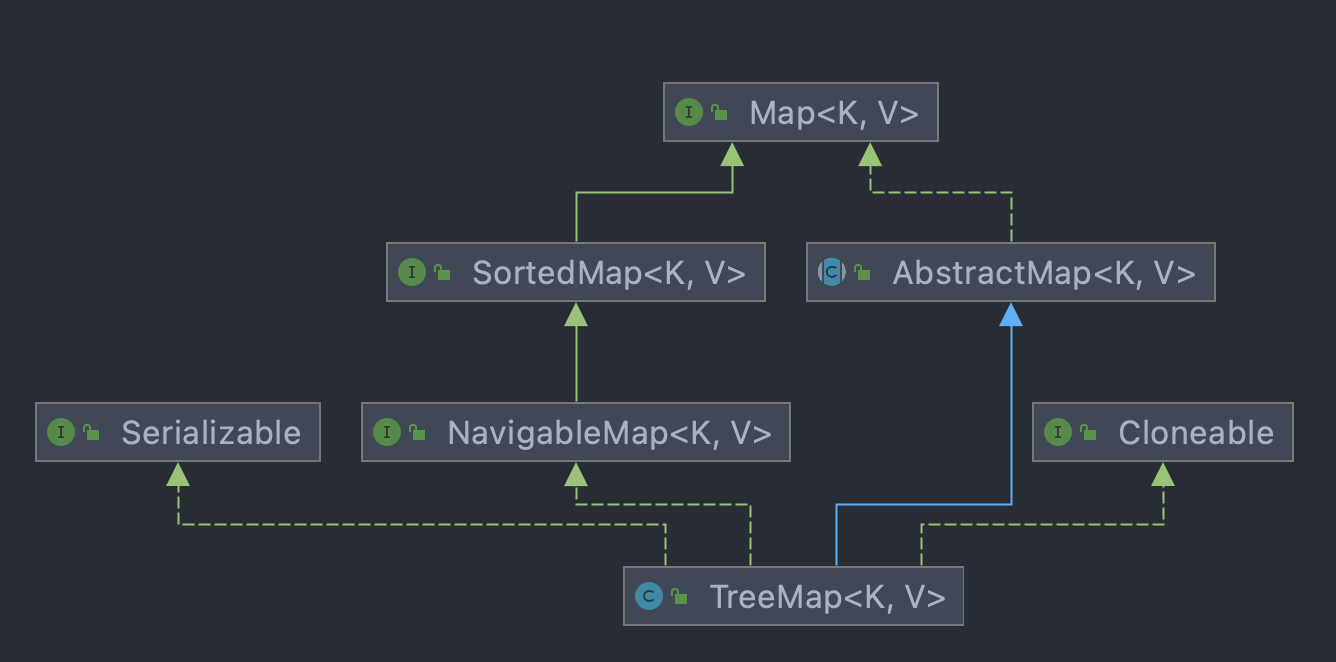
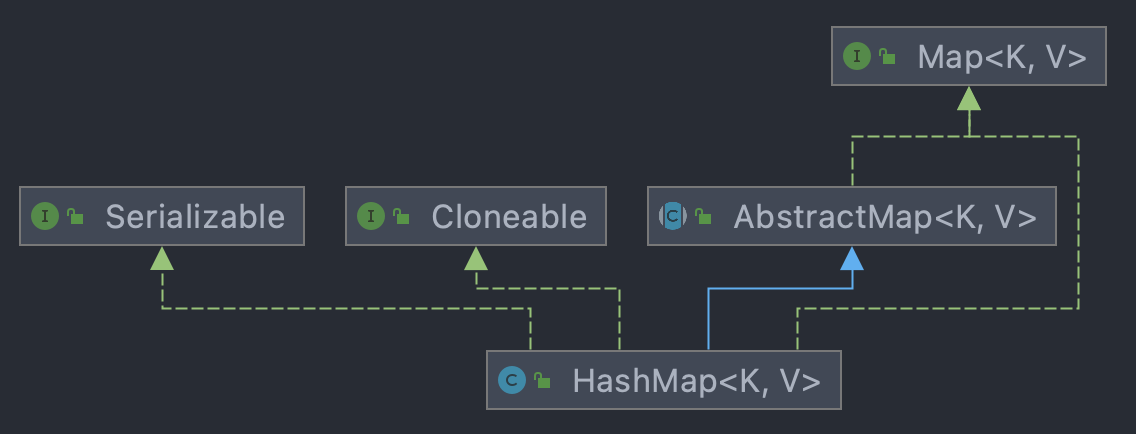
与HashMap相同之处:
- 实现了Java.io.Serializable接口;
- 实现了Cloneable接口;
- 继承了AbstractMap,并实现了Map接口;
值得注意的是:
-
实现了NavigableMap接口,对SortedMap接口进行了进一步扩展。
支持Comparator自定义插入顺序;支持多种策略的搜索获取界定操作;
-
用红黑树这种排序二叉树来保存Map中每个Entry,每个Entry被当成”红黑树”的一个节点来对待。
TreeMap特点
-
key-value 映射,key唯一,value可重复;
与HashMap同样实现了Map接口,为典型的 <key,value> 数据存储。
-
value允许null元素;
与HashMap有别,仅value支持null元素;
-
可以对元素进行排序,但读取没HashMap快;
默认字典序,支持Comparator;
-
无序集合(插入和遍历顺序不一致)
基本使用
- 与HashMap相同的部分,即Map接口部分
//Map集合的功能概述:
//1:添加功能
V put(K key,V value);//添加元素
//如果键是第一次存储,就直接存储元素,返回null
//如果键不是第一次存储,就用值把以前的值替换掉,返回以前的值
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);//以Map集合批量添加
//2:删除功能
void clear();//移除所有的键值对元素
V remove(Object key);//根据键删除键值对元素,并把值返回
//3:判断功能
boolean containsKey(Object key);//判断集合是否包含指定的键
boolean containsValue(Object value);//判断集合是否包含指定的值
boolean isEmpty();//判断集合是否为空
//4:获取功能
set<Map,Entry<E,V>> entrySet();//获取键值对的对象集合
V get(Object key);//根据键获取值
Set<K> keySet();//获取集合中所有键的集合
Collection<V> values();//获取集合中所有值的集合
//5:长度功能
int size();//返回集合中的键值对的对数
//Map遍历部分,遍历方法的泛型写法
public static <E> void printMapByEntrySet(Map<E, E> map) {
//定义泛型化的Map遍历输出方法----基于键值对Set
// A:获取所有的键值对对象的集合
Set<Map.Entry<E, E>> set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println("当前Map中元素为:");
System.out.println("key---value");
// B:遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对的对象
for (Map.Entry<E, E> me : set) {
// C:获取键和值
E key = me.getKey();
E value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " --- " + value);
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
//引入Lambda + Stream 改写
public static <E> void printMapByEntrySetL(Map<E, E> map) {
//定义泛型化的Map遍历输出方法----基于键值对Set
// A:获取所有的键值对对象的集合
Set<Map.Entry<E, E>> set = map.entrySet();
System.out.println("当前Map中元素为:");
System.out.println("key---value");
// B:遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对的对象
set.stream().forEach(Entry -> System.out.println(Entry.getKey() + " --- " + Entry.getValue()));
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
public static <E> void printMapByKeySet(Map<E, E> map) {
//定义泛型化的Map遍历输出方法----基于键Set 查询值
// A:获取所有的键
Set<E> set = map.keySet();
System.out.println("当前Map中元素为:");
System.out.println("key---value");
// B:遍历键的集合,获取得到每一个键
for (E key : set) {
// C:根据键查询值
E value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " --- " + value);
}
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
//引入Lambda + Stream 改写
public static <E> void printMapByKeySetL(Map<E, E> map) {
//定义泛型化的Map遍历输出方法----基于键Set 查询值
// A:获取所有的键
Set<E> set = map.keySet();
System.out.println("当前Map中元素为:");
System.out.println("key---value");
// B:键的集合stream流化并遍历查询并输出
set.stream().forEach(key -> System.out.println(key + " --- " + map.get(key)));
System.out.println("--------------------");
}
- SortedMap接口
//返回元素比较器。如果是自然顺序,则返回null;
Comparator<? super K> comparator();
//返回从fromKey到toKey的集合:含头不含尾
SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
//返回从头到toKey的集合:不包含toKey
SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey);
//返回从fromKey到结尾的集合:包含fromKey
SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey);
//返回集合中的第一个元素:
K firstKey();
//返回集合中的最后一个元素:
K lastKey();
//返回集合中所有key的集合:
Set<K> keySet();
//返回集合中所有value的集合:
Collection<V> values();
//返回集合中的元素映射:
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
- NavigableMap接口
//返回小于key的第一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> lowerEntry(K key);
//返回小于key的第一个键:
K lowerKey(K key);
//返回小于等于key的第一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> floorEntry(K key);
//返回小于等于key的第一个键:
K floorKey(K key);
//返回大于或者等于key的第一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> ceilingEntry(K key);
//返回大于或者等于key的第一个键:
K ceilingKey(K key);
//返回大于key的第一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> higherEntry(K key);
//返回大于key的第一个键:
K higherKey(K key);
//返回集合中第一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> firstEntry();
//返回集合中最后一个元素:
Map.Entry<K,V> lastEntry();
//返回集合中第一个元素,并从集合中删除:
Map.Entry<K,V> pollFirstEntry();
//返回集合中最后一个元素,并从集合中删除:
Map.Entry<K,V> pollLastEntry();
//返回倒序的Map集合:
NavigableMap<K,V> descendingMap();
//返回Map集合中的Key组成的Set集合:
NavigableSet<K> navigableKeySet();
//返回Map集合中倒序的Key组成的Set集合:
NavigableSet<K> descendingKeySet();
NavigableMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, boolean fromInclusive,
K toKey, boolean toInclusive);
NavigableMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey, boolean inclusive);
NavigableMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey, boolean inclusive);
SortedMap<K,V> subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap<K,V> headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap<K,V> tailMap(K fromKey);
TreeSet
TreeSet 源码比HashSet多了199行,和TreeMap类似,也内设了一些非常便利的方法调用。
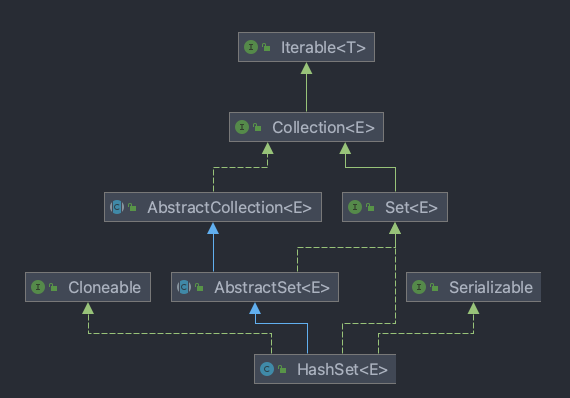
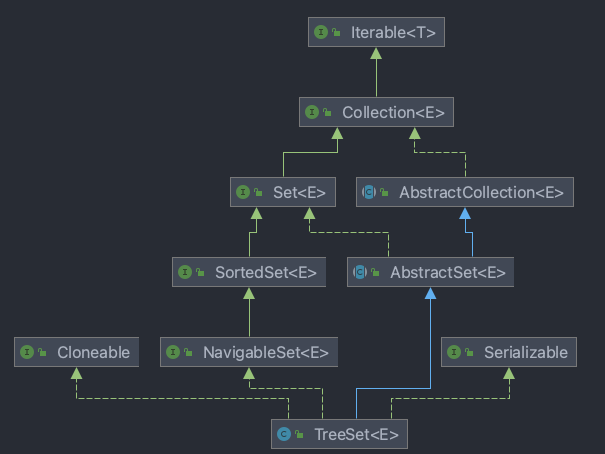
值得注意的是,TreeSet实际内部使用TreeMap存储,TreeSet元素存放于TreeMap的key,因此:TreeSet特性与TreeMap相当。
//TreeSet的构造函数通过新建一个TreeMap作为实际存储Set元素的容器
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
TreeSet特点
-
key唯一不重复;
实际存放与TreeMap的key上
//TreeSet add method public boolean add(E e) { return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;//m 为TreeMap } -
key不允许null元素;
-
可以对元素进行排序,但读取没HashSet快;
基本使用
- Set接口部分
//Map集合的功能概述:
//1:添加功能
boolean add(E e);//添加元素
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//以集合方式批量添加
//2:删除功能
void clear();//移除所有的元素
boolean remove(Object o);//删除元素
boolean removeAll(Collection<? extends E> c);//以集合方式批量删除
//3:判断功能
boolean contains(Object o);//判断集合是否包含指定元素
boolean isEmpty();//判断集合是否为空
//4:长度功能
int size();//返回集合中的元素个数
- SortedSet接口部分
Comparator<? super E> comparator();
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
E first();
E last();
NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
E toElement, boolean toInclusive);//子集
NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {
return new TreeSet<>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));
- NavigableSet接口部分
E lower(E e);//返回小于e的第一个元素,没有则null
E floor(E e);//返回小于等于e的第一个元素,没有则null
E ceiling(E e);//返回大于等于e的第一个元素,没有则null
E higher(E e);//返回大于e的第一个元素,没有则null
E pollFirst();//取出第一个元素
E pollLast();//取出最后一个元素
NavigableSet<E> descendingSet();//逆序
NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
E toElement, boolean toInclusive);//子集 from to 可配置
NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive);//to 可配置
NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive);//from 可配置
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);//[from,to)
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);//to 不包含 [head to)
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);//from 不包含 (from to]
测试用例:
TreeSet<Integer> treeSet=new TreeSet<>();
List<Integer> listTest = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
treeSet.addAll(listTest);
//treeSet.removeAll(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6));
System.out.println("原始Set:");
treeSet.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
System.out.println("subSet(7,10):");
treeSet.subSet(7,10).
stream().
forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,
// E toElement, boolean toInclusive);
System.out.println("subSet(7,true,10,true).descendingSet():");
treeSet.subSet(7,true,10,true).
descendingSet().
stream().
forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
System.out.println("headSet(5):");
treeSet.headSet(5).stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive);
System.out.println("headSet(5,false):");
treeSet.headSet(5,false).stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive);
System.out.println("tailSet(5):");
treeSet.tailSet(5).stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
//SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
System.out.println("tailSet(5,false):");
treeSet.tailSet(5,false).stream().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------");
