链表
放在最前面
3.从尾到头打印链表
- 1.利用栈
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.addLast(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
list.add(stack.removeLast());
}
return list;
}
}
- 2.递归
逆序打印链表 1->2->3(3,2,1),可以先逆序打印链表 2->3(3,2),最后再打印第一个节点 1。而链表 2->3 可以看成一个新的链表,要逆序打印该链表可以继续使用求解函数,也就是在求解函数中调用自己,这就是递归函数。
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list;//先写在外面 因为需要递归
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
if(listNode != null){
printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next);
list.add(listNode.val);
}
return list;
}
}
-
3.反转链表再输出
-
使用头插法可以得到一个逆序的链表。
头结点和第一个节点的区别:
- 头结点是在头插法中使用的一个额外节点,这个节点不存储值;
- 第一个节点就是链表的第一个真正存储值的节点。
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
// 头插法构建逆序链表
//建立头节点 辅助使用 head.next=null 默认构造
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
while (listNode != null) {
//先记录下一节点
ListNode pnext = listNode.next;
//头插法第一步 插入listNode在head后
listNode.next = head.next;
//更新头节点head 指向插入的节点listNode
head.next = listNode;
//listNode 向后步进
listNode = pnext;
}
// 构建 ArrayList
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
//跳过我们设置的头节点
head = head.next;
while (head != null) {
res.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
return res;
}
}
14.链表中倒数第k个结点
1.两次遍历
- 链表是单链表,没有保存长度信息第一次遍历计算length。
- 第二次遍历找到第length - k个节点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
//k为0和head为null的情况返回null
if(head == null || k == 0) return null;
ListNode tmp = head;
int len=0;
while(tmp!=null){
tmp=tmp.next;
len++;
}
if(len<k){
return null;
}else{
for(int i=0;i<len-k;i++){
head=head.next;
}
return head;
}//else end
}//method end
}
2.双指针
准备两个指针:left和 right
- right 先向右移动 k 位,此时 index(right) - index(left) = k
- left 和 right 一起向右移动,直到 right 抵达边界
- 由于index(right) - index(left) = k,所以index(left) = index(right) - k = length - k。也就是 left 指针移动到了倒数第 k 个位置
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
//k为0和head为null的情况返回null
if(head == null || k == 0) return null;
ListNode left = head,right = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if(right == null){
return null;
}//快指针行进不到k步就为null证明 链表长度不够k 即返回null
right = right.next;
}//fori end
while(true){
//right为null时,left到达了位置,直接返回left
if(right == null){
return left;
}
right = right.next;
left = left.next;
}//while end
}
}
15.反转链表
1.头插法
头结点和第一个节点的区别:
头结点是在头插法中使用的一个额外节点,这个节点不存储值;
第一个节点就是链表的第一个真正存储值的节点。
下文的head与prehead的区别
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {//head 为第一个节点 是原链表真正存储值的节点
// 头插法构建逆序链表
//建立头节点 辅助使用 prehead.next=null 默认构造 prehead 是额外节点
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
while (head != null) {
//先记录下一节点
ListNode pnext = head.next;
//头插法第一步 插入listNode在prehead后
head.next = prehead.next;
//更新头节点prehead 指向插入的节点listNode
prehead.next = head;
//listNode 向后步进
head = pnext;
}
//跳过我们设置的额外头节点
return prehead.next;
}
}
2.双指针就地逆序
题目所给的是单链表,先想一下反转后的样子:最后一个结点指向倒数第二个,倒数第二个指向倒数第三个,……,第二个指向第一个,第一个指向null;
知道了反转后各个结点指向哪之后,就需要开始调整每个结点的next指针。
这就需要把结点挨个从链表上摘下来,做调整;
这个调整过程需要两个指针辅助:pre记录其前一个结点位置,好让该结点的next指针指向前一个结点,但是在指向前一个结点前需要用一个指针p记录后一个结点地址,避免结点丢失。
例子:
以head结点为例步骤如下:
- 1.反转后head是指向null,所以未反转的时候其前一个结点应该是null,初始化pre指针为null;
- 2.用p指针记录head的下一个结点head.next;
- 3.从链表上摘下head,即让head.next指向pre;
- 4.此时已完成head结点的摘取及与前一个节点的连接,则我们需要操作下一个结点:故需移动pre和head,让pre指向head,head指向下一个节点。
重复这四个操作直到head走完原链表,指向null时,循环结束,返回pre。
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
//初始化pre指针,用于记录当前结点的前一个结点地址
ListNode pre = null;
//初始化p指针,用于记录当前结点的下一个结点地址
ListNode pnext = null;
//head指向null时,循环终止。
while(head != null){
//先用p指针记录当前结点的下一个结点地址。
pnext = head.next;
//让被当前结点与链表断开并指向前一个结点pre。
head.next = pre;
//pre指针指向当前结点
pre = head;
//head指向p(保存着原链表中head的下一个结点地址)
head = pnext;
}
return pre;//当循环结束时,pre所指的就是反转链表的头结点
}
}
16.合并两个排序的链表
常规版本
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
ListNode head;
if(list1.val>list2.val){
head=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}else{
head=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}
ListNode tmp=head;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val>list2.val){
tmp.next=list2;
tmp=tmp.next;
list2=list2.next;
}else{
tmp.next=list1;
tmp=tmp.next;
list1=list1.next;
}
}
if(list1!=null){
tmp.next=list1;
}
if(list2!=null){
tmp.next=list2;
}
return head;
}
}
适当优化
确定head那里用得太多 而且if那部分代码其实和后面重合了 可以考虑引入额外的头节点 节省代码
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null) return list2;
if(list2 == null) return list1;
ListNode node = new ListNode(-1),prehead = node;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if (list1.val <= list2.val) {
node.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
node.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
node = node.next;
}//while end
node.next = list1 == null? list2 : list1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
其实 也可以递归实现
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null){
return list2;
}
if(list2==null){
return list1;
}
if(list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = Merge(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = Merge(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}//method end
}
25.复杂链表的复制
- 利用map的映射
map的key存储链表的元素。
map的value是新new的元素,label已经确定,next和radom要在p2循环链表的时候进行指定。
/*
public class RandomListNode {
int label;
RandomListNode next = null;
RandomListNode random = null;
RandomListNode(int label) {
this.label = label;
}
}
*/
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead)
{
if(pHead == null) return null;
Map<RandomListNode,RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
RandomListNode p1 = pHead;
RandomListNode p2 = pHead;
while(p1!=null){
map.put(p1,new RandomListNode(p1.label));
p1 = p1.next;
}
while(p2!=null){
if(p2.next != null){
map.get(p2).next = map.get(p2.next);
}else{
map.get(p2).next = null;
}
map.get(p2).random = map.get(p2.random);
p2 = p2.next;
}
return map.get(pHead);
}
}
- 原地复制拆分
思路
第一步,在每个节点的后面插入复制的节点。
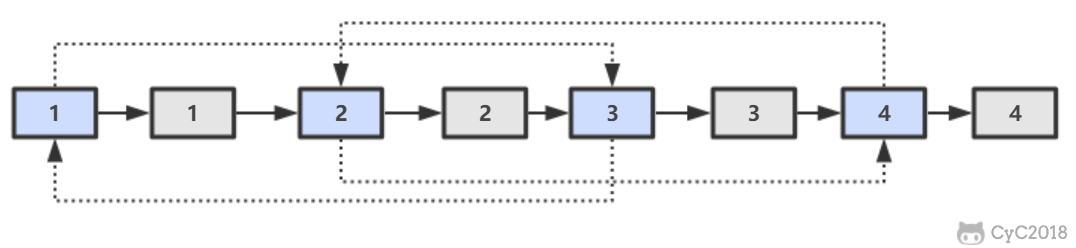
第二步,对复制节点的 random 链接进行赋值。
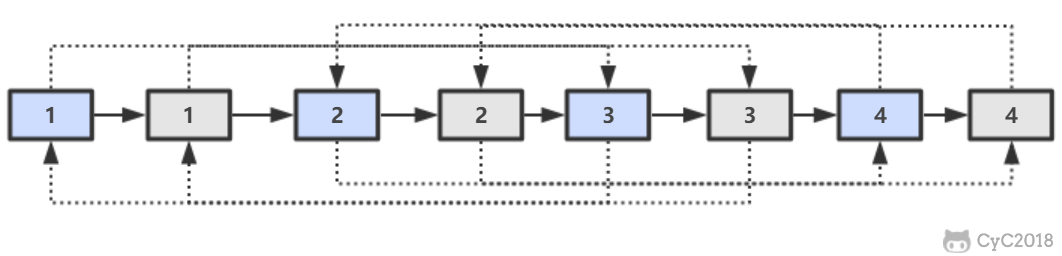
第三步,拆分。
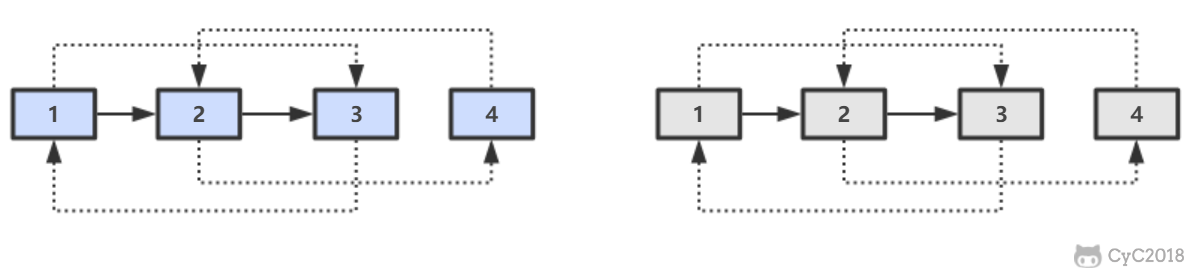
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null)
return null;
// 插入新节点
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
clone.next = cur.next;
cur.next = clone;
cur = clone.next;
}
// 建立 random 链接
cur = pHead;
while (cur != null) {
RandomListNode clone = cur.next;
if (cur.random != null)
clone.random = cur.random.next;//指向新复制的那个 所以有个next
cur = clone.next;
}
// 拆分
cur = pHead;
RandomListNode pCloneHead = pHead.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
RandomListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = next.next;
cur = next;
}
return pCloneHead;
}
36.两个链表的第一个公共结点
- 思路1:校正指针初始位置
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
int len1=length(pHead1);
int len2=length(pHead2);
if(len1>len2){
ListNode res=FindFirstCommonNode(pHead2,pHead1);
return res;
}else{
int k=len2-len1;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}
while(pHead2!=null&&pHead1!=null){
if(pHead1==pHead2){
return pHead1;
}
pHead1=pHead1.next;
pHead2=pHead2.next;
}
}
return null;
}
public int length(ListNode p) {
int res=0;
while(p!=null){
res++;
p=p.next;
}
return res;
}
}
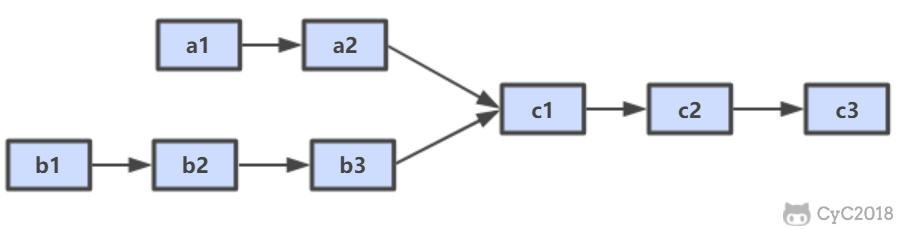
- 思路2:循环/构造等长链表
a1 a2 c1 c2 c3 /b1 b2 b3 c1 c2 c3
b1 b2 b3 c1 c2 c3 /a1 a2 c1 c2 c3
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) return null;
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while(p1.val != p2.val){
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
if(p1 == null && p2 == null) return null;
if(p1 == null) p1 = pHead2;
if(p2 == null) p2 = pHead1;
}
return p1;
}
}
55.链表中环的入口结点
- 快慢指针

fast 步进为2,slow 步进为1,有环时,fast与slow一定会在环内相遇
当fast与slow相遇时,fast走过的距离为a + b + c + b,而slow走过的距离为a + b,因为fast是slow速度的两倍,则有a+b+c+b = 2*(a+b),登出a=c;
相遇后将fast移到头指针,fast和slow同时步进1移动,找到根据a=c找到入口。
代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null) return null;
ListNode slow = pHead, fast = pHead;
do{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}while(slow != fast);
fast = pHead;
while(fast != slow){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
56.删除链表中重复的结点
非递归写法
我们在考虑的情况中,如果头节点开始就重复,我们就处理很起来多了一种情况就需要额外处理,所以我们添加一个头节点,变成带头节点,保证了头节点开始不会重复。
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead)
{
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) {
return pHead;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1); // 新建一个头结点,防止链表中头结点是重复节点被删除。
ListNode trail = head;
while (pHead != null) {
ListNode pnext = pHead.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (pnext != null && pHead.val == pnext.val) {
pnext = pnext.next;
flag = true;
}//pnext重复性验证
if (!flag) {
trail.next = pHead;
trail = trail.next;
}
pHead = pnext;
}
trail.next = null; // 1->2->3->3->3
return head.next;
}//method end
}
递归写法
要点是对重复元素和不重复元素的分别处理:
- 重复元素就一直向后找,直到第一个不一样的元素出现为止,然后继续判断此元素是否是重复元素。
- 不重复元素就直接next指向。
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null || pHead.next == null) return pHead;
//对重复元素进行处理,将node一直指向此所有重复元素后一位,然后递归继续进行判断,
if(pHead.val == pHead.next.val){
ListNode node = pHead.next;
while(node != null && node.val == pHead.val){
node = node.next;
}
//排除了前面的重复元素,重新递归
return deleteDuplication(node);
}else{//对不重复元素,直接进行next指向处理
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
}
return pHead;
}
}
